 Table of Contents
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Information Security Risk Management (ISRM)?
- Compliance and regulatory requirements
- Establishing a risk management framework
- Selecting and implementing a security framework
- Fostering an information security culture
- IT Asset Management and risk assessment
- What is Third-Party Security Risk Management (TPSRM)?
- What is Application Security Risk Management (ASRM)?
- Risk response and mitigation strategies
- The role of GRC platforms in ISRM
- Measurement and reporting
- Conclusion and future directions
Introduction
Information Security Risk Management (ISRM) is essential for any modern organization operating in the digital world. As cyber threats grow more sophisticated, protecting sensitive data, building resilience, and maintaining compliance are increasingly important. With the global cost of cybercrime projected to hit $10.5 trillion by 2025, getting started with (or optimizing) your ISRM program is no longer optional; it’s imperative.
With the global cost of cybercrime projected to hit $10.5 trillion by 2025, getting started with an Information Security Risk Management (ISRM) program is imperative.
But ISRM isn’t about responding to incidents but proactively managing risks to prevent them. It’s a systematic approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating information security risks. It enables organizations to protect sensitive data, ensure system reliability, maintain data accuracy and operational continuity, and adhere to global regulations.
This guide from SaltyCloud provides a comprehensive yet accessible pathway for developing an Information Security Risk Management program. It demystifies the complexity surrounding ISRM and offers clear guidance for practical implementation. Designed for a diverse audience, including information security analysts, CISOs, GRC analysts, and IT managers, this guide enhances your organization’s approach to managing information security risks.
What is Information Security Risk Management (ISRM)?
Information Security Risk Management (ISRM) involves actively managing risks associated with information technology. It’s a collaborative effort involving multiple stakeholders working together to protect their assets’ confidentiality, integrity, and availability. An ISRM program identifies and manages risks that could compromise critical data and systems at the heart of modern businesses.
At its core, ISRM is about making well-informed decisions. It’s a strategic blend of pinpointing potential information security risks, evaluating their likelihood and potential impact, and deploying the appropriate measures to counteract them.
Information Security Risk Management is about making well-informed decisions. It’s a blend of pinpointing information security risks, evaluating their impact, and deploying measures to counteract them.
Why is ISRM important?
ISRM is important because it helps organizations protect data integrity and ensures uninterrupted business operations. It’s a critical function that supports an organization’s resilience against potential cyber threats, unauthorized access, and other vulnerabilities that can disrupt business continuity and damage reputation.
Compliance and regulatory requirements
The evolving regulatory compliance landscape increasingly requires organizations to adopt Information Security Risk Management programs. Driven by regulations such as the HIPAA Security Rule, the GLBA Safeguards Rule, the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC), and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), there is a clear shift from reactive to proactive approaches in information security.
But these regulations aren’t just legal obligations — they provide a structured approach to safeguarding sensitive data like intellectual property against cyber threats and vulnerabilities. By adhering to these standards, your organization can ensure its risk management processes are aligned with global best practices, helping avoid non-compliance penalties and data breaches.
Compliance is more than a checklist in ISRM. It informs how organizations assess and prioritize risks, offering a framework for identifying potential threats and implementing security controls. It shapes an organization’s overall approach to managing information security risks.
In the context of ISRM, compliance is more than a checklist. It’s a dynamic component of a risk management strategy, informing how organizations assess and prioritize risks. Compliance requirements offer a framework for identifying potential threats and implementing security controls This, in turn, shapes your organization’s overall approach to managing information security risks.
At the same time, staying current with relevant regulations and standards is a continuous effort in ISRM. Organizations must cultivate a culture of proactive learning and collaboration to do so. Regular training sessions and active engagement with legal and compliance teams are essential.
How should global or highly distributed organizations manage ISRM?
Global or highly distributed organizations face unique challenges in ISRM because they are often exposed to multiple regulations across different regions and sectors. A centralized ISRM program is essential but must be flexible enough to adapt to regional regulatory demands.
An ISRM program must be flexible enough to adapt to regional regulatory demands.
For these organizations, ISRM involves managing risks at a local level while maintaining visibility and control at a global scale. It requires a structure where regional security teams, well-versed in local compliance requirements, work together to ensure a cohesive approach to risk management. Collaboration is crucial for creating a uniform security culture across your organization while respecting regulatory nuances.
Establishing a risk management framework
A risk management framework is a strategic blueprint for managing information security risks. Unlike a security framework, which details specific security measures and controls, an enterprise risk management framework is like the master plan that guides your overall risk strategy.\

A risk management framework is vital for developing an effective ISRM program. It’s a strategic blueprint for managing information security risks — the master plan that guides your overall risk strategy.
For example, NIST 800-39 outlines the overall approach to identifying and managing cybersecurity risks. Meanwhile, a security framework like NIST CSF or ISO/IEC 27001 offers more detailed guidelines for implementing specific security measures.
What are the core risk management frameworks available?
To guide their ISRM efforts, organizations have access to several core risk management frameworks, each with a unique approach and focus:
- NIST SP 800-39: This framework provides a comprehensive approach to managing information security risks. It covers the full spectrum of risk management processes, including framing, assessing, responding to, and monitoring risk.
- ISO/IEC 27005: Specifically focused on risk management within the context of information security, ISO/IEC 27005 offers guidelines for establishing, implementing, and continuously improving information security risk management within an organization.
When choosing between NIST SP 800-39 and ISO/IEC 27005 for Information Security Risk Management, organizations typically consider regulatory requirements, the scope of their operations, and industry best practices.
US organizations and local, state, and federal agencies often prefer NIST, while international organizations may lean towards ISO for its global recognition. The choice also depends on existing processes, global operations, and the resources available for implementation and maintenance. Information security teams should study both closely to identify which works best for them.
How can an organization tailor risk management frameworks to meet its specific needs?
To tailor risk management frameworks like NIST SP 800-39 or ISO/IEC 27005, organizations must align them with their unique risks, business objectives, and regulatory context. This involves adapting the frameworks to fit an organization’s vulnerabilities, team dynamics, and collaborative practices. By customizing these guidelines, companies can ensure their risk management programs are compliant and can effectively mitigate unique threats while supporting their specific business goals.
Integrating risk management frameworks requires a thoughtful approach and a thorough understanding of your organization’s current workflows, processes, and risk management approach.
Crucial steps include evaluating how existing practices align with the proposed framework and identifying potential areas for enhancement or disruption. Central to this integration is fostering a culture of risk awareness, accountability, and information security.
Collaboration efforts across departments are essential to ensure new measures effectively complement and refine existing risk management activities. Strategically trialing the process in high-risk business units can be highly effective.
Integrating risk management frameworks requires a thoughtful approach and a thorough understanding of your organization’s current workflows, processes, and risk management approach.
A Collaborative GRC Platform like Isora is invaluable. Isora facilitates the integration of these risk management frameworks with tools for automated IT asset inventory management, third-party inventory management, questionnaire-based assessments, scorecards, reports, and a risk register. This approach ensures a smooth rollout, enabling organizational participation and reinforcing a cohesive risk management strategy.
Selecting and implementing a security framework
Security frameworks provide the guidelines and best practices to protect your organization’s information assets. Understanding what these frameworks offer and how they can be tailored to fit your organization’s specific needs is key to enhancing its security posture. This section explores available frameworks, their importance, and the best practices for implementing and customizing them for your risk management program.
What is a security framework, and why is it important?
A security framework is a set of policies, standards, and guidelines designed to manage and mitigate cybersecurity risks. It’s a roadmap for organizations that provides a structured approach to securing information systems. Implementing a security framework helps standardize practices, ensure compliance, and strengthen an organization’s overall security posture.
A security framework provides the guidelines and best practices to protect your organization’s information assets. It’s a roadmap for securing information systems, standardizing practices, ensuring compliance, and strengthening your security posture.
Which security frameworks are best suited for different organizational goals?
Choosing the right security framework depends on your organization’s specific needs, risk profile, and compliance requirements. Some of the most widely recognized frameworks include:
- NIST CSF: Best for organizations seeking a flexible, high-level framework adaptable across various sectors for improving cybersecurity practices.
- NIST 800-171: Best for non-federal entities that handle controlled unclassified information (CUI), providing specific guidelines for protecting this sensitive data.
- NIST 800-53: Best for federal information systems and organizations, offering an extensive array of security controls for comprehensive cybersecurity management.
- CIS Controls: Best for organizations looking for a focused, manageable set of high-impact cybersecurity actions, avoiding the complexity of more extensive frameworks.
- ISO27001: Best for organizations aiming to comply with international standards, providing a framework suitable for any industry or country.
- SOC2: Best for cloud service providers managing customer data, focusing on non-financial controls related to data security and privacy.
Each framework has its strengths and is designed to treat risks within particular cybersecurity aspects in various organizational contexts.
How to align its security frameworks with broader goals
Aligning a security framework with your organization’s broader goals involves clearly understanding business objectives and specific security requirements. It ensures the framework supports your organizational strategy and enhances security posture. This might mean customizing the framework to fit your business’s unique structure and risk landscape. It could also involve prioritizing certain framework aspects to align with your organization’s most pressing security concerns.
Best practices for implementing and customizing security controls
Implementing and customizing security controls within these frameworks requires a systematic approach:
- Assessment: Evaluate your organization’s security posture and regulatory requirements to identify specific needs and vulnerabilities.
- Control Selection: Choose security controls that align with your chosen framework and your organization’s unique requirements, considering various compliance needs across different units.
- Policy Implementation: Codify these controls into policies and roll them out, ensuring they integrate with existing processes and are suitable for enterprise and unit/team-level solutions.
- Compliance and Monitoring: Monitor compliance with these controls, track gaps in a risk register, and ensure accountability across the organization.
- Regular Updates: Continuously review and update your policies and controls to respond to evolving threats and organizational changes.
Fostering an information security culture
Nurturing a security-focused mindset across your organization is beneficial and essential for an effective risk management program. This section examines the strategies that embed security awareness into the fabric of organizational behavior so that every team member and risk owner actively protects your organization’s digital assets.
Why cultivating a security culture is essential for effective risk management
Building a culture of information security is critical for managing risk. It goes beyond implementing policies and technologies — it’s about ingraining security awareness into every aspect of your organization’s operations. A strong security culture ensures that every team member, especially risk owners, understands the importance of information security and plays a role in protecting your organization’s assets. This collective awareness and proactive attitude are key in preventing security incidents and responding effectively when they do occur.
Cultivating a security culture is critical for effective risk management. It’s about ingraining security awareness into every aspect of your organization’s operations so that every team member (including risk owners) actively protects your organization’s digital assets.
In a successful security culture, information security is not seen as a responsibility solely for IT or security teams. Instead, it becomes a shared commitment across the organization. This approach leads to more responsible, vigilant behavior, reducing the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches due to human error.
Strategies to promote risk awareness
To promote risk awareness, your organization can employ several strategies:
- Regular training and education: Provide ongoing education and training sessions to keep staff updated on the latest security threats and best practices.
- Engaging communication: Use clear, concise, and engaging communication to reinforce the importance of security and ensure understanding across all levels of the organization.
- Gamification: Introduce gamification elements, such as challenges and rewards, to make learning about cybersecurity more engaging and memorable.
- Leadership involvement: Encourage leaders to actively participate in and endorse security initiatives, demonstrating the organization’s commitment to security from the top down.
- Feedback mechanisms: Implement channels for employees to report potential security issues and provide feedback on the organization’s security policies and practices.
Creating a culture of security is an ongoing process that should evolve with your organization and the changing landscape of cybersecurity threats. It requires commitment, communication, and continuous improvement.
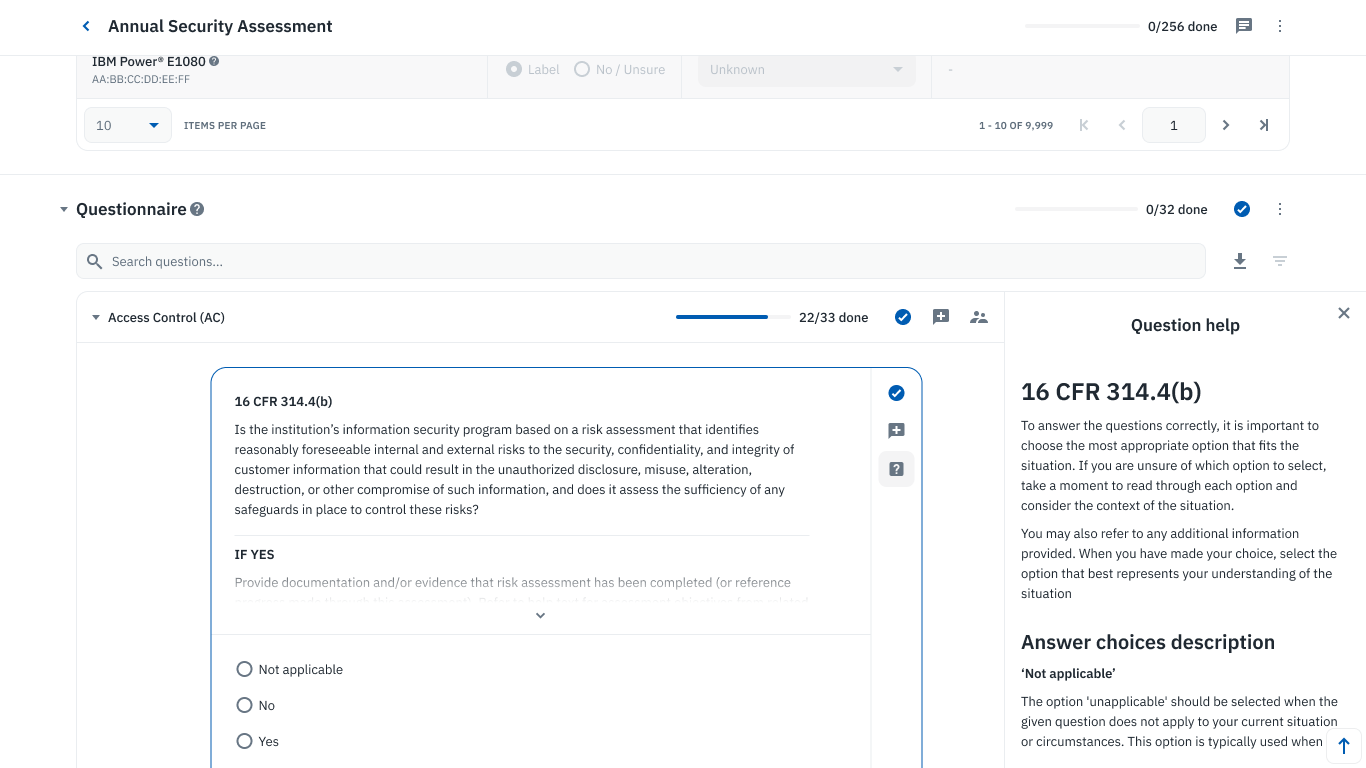
Collaborative questionnaire on Isora GRC.
Creating a culture of security is an ongoing process that should evolve with your organization and the changing cyber threat landscape. It requires commitment, communication, and continuous improvement.
Isora GRC from SaltyCloud is a central, collaborative platform that unites team members in understanding and meeting security requirements. It streamlines the process of gathering evidence, assigning risk owners, answering security questions, identifying and tracking risks, and working collectively toward cyber resilience.
IT Asset Management and risk assessment
Managing IT assets and conducting thorough risk assessments are vital to identifying and mitigating potential security threats. This section focuses on the role of IT Asset Management (ITAM) and risk assessments in ISRM.
Why scoping is important for ISRM
Scoping defines the boundaries and focus of your security efforts. Ultimately, organizations can better allocate resources and prioritize security measures by clearly identifying critical assets — such as data, hardware, and software. Scoping also prevents the dilution of security efforts across too broad an area, allowing for a more targeted and precise approach to mitigating risks.
Why IT Asset Management is important in ISRM
IT Asset Management plays a pivotal role in ISRM. It involves tracking and managing your organization’s physical and digital assets, which is essential for understanding potential risks.
IT Asset Management involves tracking and managing your organization’s physical and digital assets. An asset inventory makes it easier to identify vulnerabilities, assess the level of risk, and implement safeguards.
Through effective ITAM, organizations can gain visibility into their asset inventory, making it easier to identify vulnerabilities, assess the level of risk each asset faces, and implement appropriate safeguards. This visibility is key to ensuring no critical asset is overlooked in risk management.
Why risk assessments are important in ISRM
Risk assessments are the backbone of effective ISRM. They involve evaluating potential threats to an organization and determining the likelihood and impact of these threats.
Risk assessments allow organizations to categorize risks, prioritize response strategies, and decide where to focus risk mitigation strategies.
The risk assessment process starts with identifying potential threats, achieved through automated methods like installing agents and semi-automated approaches such as questionnaires and surveys. Then, each identified risk is evaluated based on its likelihood and impact on the organization’s assets, following guidelines from standards like NIST 800-39 or ISO/IEC 27005. The results can be documented in a risk register.
Through risk assessments, your organization can categorize risks, prioritize its response strategies, and make informed decisions about where to focus its mitigation efforts. This process is vital for identifying vulnerabilities before they can be exploited and ensuring that your organization’s security posture is proactive and resilient.
Incorporating tools like Isora GRC can significantly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of risk assessments. By automating the assessment process, Isora GRC enables organizations to conduct thorough evaluations with fewer resources, ensuring they can quickly adapt to new threats and maintain a strong security posture.
What is Third-Party Security Risk Management (TPSRM)?
Third-Party Security Risk Management (TPSRM) is critical to your organization’s Information Security Risk Management program. It addresses the risks external vendors and service providers pose, ensuring that their security practices align with your organization’s standards and compliance requirements.
Third-Party Security Risk Management is about managing risks associated with external entities like vendors, suppliers, and service providers.
TPSRM involves evaluating and monitoring the security measures of these external parties to ensure they meet your organization’s data protection and cybersecurity standards. This process is critical for preventing a data breach or cyberattacks arising from third-party vulnerabilities. By managing these risks, your organization can protect sensitive data, maintain compliance with regulatory standards, and preserve its reputation.
Incorporating comprehensive TPSRM strategies is essential for a holistic approach to risk management. It ensures that security considerations extend beyond your organization’s immediate boundaries, encompassing the broader network of third-party relationships.
What is Application Security Risk Management (ASRM)?
Application Security Risk Management (ASRM) targets the risks associated with an organization’s software applications. It’s a critical component of ISRM, focusing on identifying, assessing, and mitigating vulnerabilities in internally developed and third-party applications.
Application Security Risk Management is a critical component of ISRM, focused on identifying, assessing, and mitigating vulnerabilities in internally developed and third-party software applications.
ASRM is important because applications are often a primary target for cybercriminals. Weaknesses in application security can lead to unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber threats. Effective ASRM involves regularly reviewing and securing applications throughout their lifecycle, from development to deployment and maintenance.
Implementing ASRM helps protect sensitive information, ensures compliance with security standards, and upholds the integrity of your organization’s IT infrastructure. It is a proactive step towards a comprehensive security posture, addressing potential risks in the ever-evolving application development and usage landscape.
Risk response and mitigation strategies
Responding to and mitigating risks are central to Information Security Risk Management. This section explores key strategies and tools organizations can use to address identified risks.
The role of a risk register in ISRM
A risk register is a fundamental tool in Information Security Risk Management. It is a centralized repository for documenting identified risks, risk assessments, and management strategies.
A risk register is a centralized repository for documenting identified risks, risk assessments, and management strategies. It’s essential for maintaining an organized and transparent approach to risk management.
The risk register aids in tracking and monitoring risks over time, ensuring that all potential threats are accounted for and addressed appropriately. This tool is essential for maintaining an organized and transparent approach to risk management, enabling organizations to respond swiftly and effectively to emerging threats.
Isora’s collaborative risk register seamlessly integrates with your organization’s risk identification processes. Using questionnaires and surveys to uncover security gaps, Isora enables you to log these findings into a comprehensive risk register directly. This centralized platform is designed to efficiently manage and monitor risk treatment plans, assign ownership, set due dates, and more. It empowers teams to effectively track and manage their risks in one unified location, enhancing the overall efficiency and clarity of the risk management process.
How to develop risk response plans
Developing comprehensive risk response plans involves a few key steps:
- Assess and prioritize risks: Evaluate each identified risk’s potential impact and likelihood.
- Develop response strategies: For each risk, create tailored response strategies, including avoidance, mitigation, transfer, acceptance, or incorporating business continuity plans to maintain critical operations during and after a risk event.
- Allocate resources: Determine the necessary resources, including budget, personnel, and technology, to implement these strategies effectively.
- Document and communicate plans: Clearly document each response plan and communicate them across the organization. Ensure that all stakeholders understand their roles and responsibilities in executing these plans.
Why collaboration is important in risk management
Collaboration brings together diverse perspectives and expertise, leading to more robust and effective risk management strategies. Engaging various departments and stakeholders ensures a complete understanding of risks and their potential impact. Collaborative efforts also foster a shared sense of responsibility and commitment to an organization’s security posture.
Collaboration brings diverse perspectives and expertise together for more robust and effective risk management strategies. It fosters a shared sense of responsibility and commitment to an organization’s security posture.
How to allocate resources for managing risks effectively
Effective resource allocation for risk management involves:
- Prioritizing high-risk areas: Focus resources on areas with the highest risk potential.
- Balancing proactive and reactive measures: Allocate resources to preventative measures and responsive capabilities for emerging threats.
- Regular review and adjustment: Continuously assess the effectiveness of allocated resources and adjust as necessary to address evolving risks and organizational changes.
Effective risk response and mitigation are dynamic processes that require ongoing attention and adaptation. By employing these strategies, organizations can ensure a resilient and responsive approach to managing information security risks.
The role of GRC platforms in ISRM
Integrating Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC) platforms into Information Security Risk Management can be transformative. This section explores how GRC platforms like Isora GRC streamline and enhance ISRM processes.
What is security GRC software?
Security Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance software is designed to streamline and integrate these three critical aspects of information security. GRC software supports organizations in managing their security policies, assessing risks, and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations.
GRC software like Isora GRC helps organizations collaboratively manage security policies, assess risks, and ensure regulatory compliance with an organized and consistent approach.
GRC software helps maintain an organized and consistent approach to managing security risks by providing a centralized platform.
Which security GRC software is best for ISRM?
Choosing the right GRC software for ISRM depends on your organization’s specific needs and context. Factors to consider include your organization’s size, IT environment’s complexity, and specific regulatory requirements.
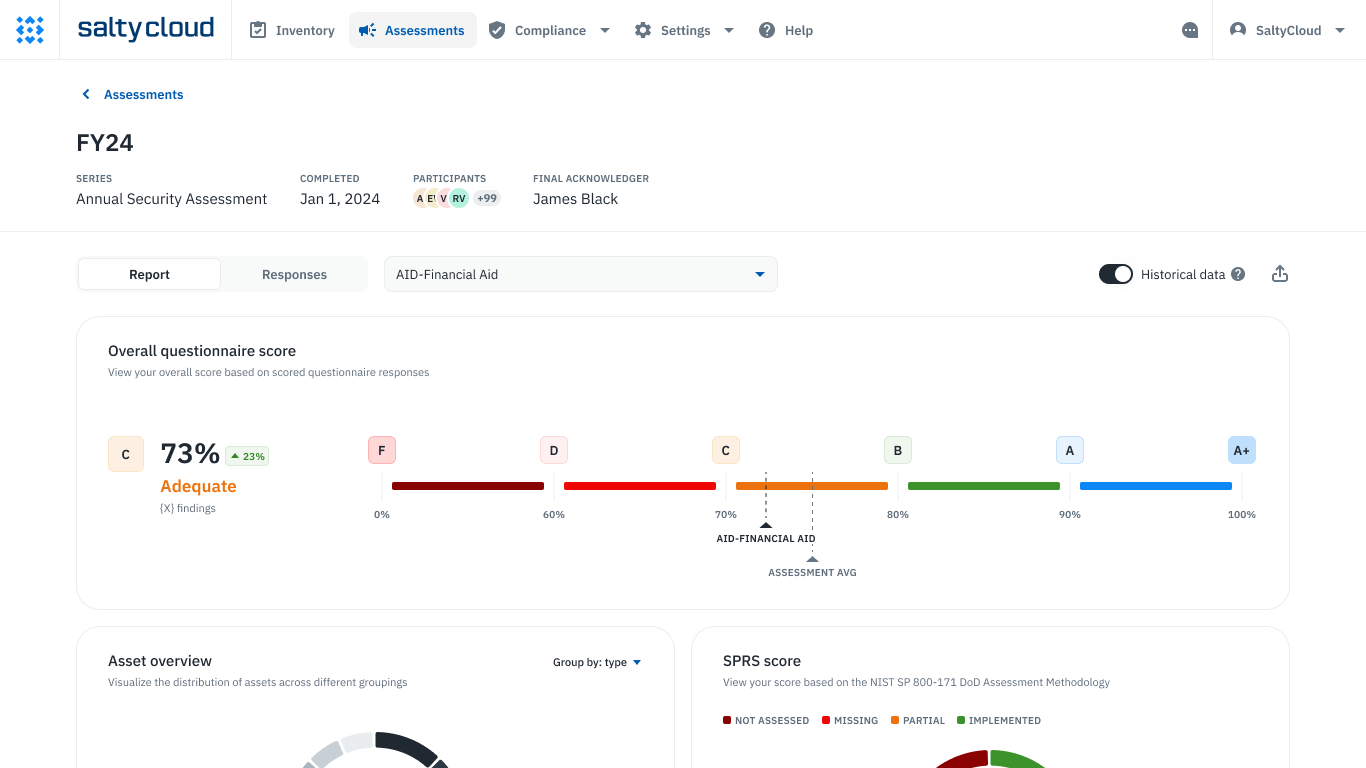
Assessment scorecards and reports in Isora GRC.
Choosing the right GRC software for your organization depends on its specific needs and context. Factors like size, the complexity of your IT environment, and specific regulatory requirements all play a role in this decision.
Isora is a collaborative GRC platform that empowers everyone to own risk together with user-friendly and flexible tools. With Isora, teams can stay agile and responsive to growing changes, fostering a resilient organizational culture. Isora is best suited for managing complex security frameworks, asset inventories, and third-party vendor ecosystems, making it ideal for organizations with diverse teams and extensive operational needs.
How GRC tools can be used for effective risk monitoring and management
GRC tools like Isora GRC can be used for effective risk monitoring and management by:
- Automating risk assessments: Simplify and speed up the risk assessment process, ensuring comprehensive coverage.
- Providing real-time visibility: A clear view of the organization’s risk posture allows for prompt identification and response to emerging threats.
- Streamlining compliance processes: Facilitate easier adherence to regulatory standards by keeping track of requirements and changes.
- Enhancing decision-making: Deliver insightful reports and analytics that support informed decision-making in risk management strategies.
By integrating these tools into their ISRM programs, organizations can achieve a more efficient, accurate, and proactive approach to managing security risks.
Measurement and reporting
Measuring and reporting progress is key to understanding and enhancing security efforts. This section examines the role of metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in evaluating the effectiveness of ISRM initiatives.
Metrics and KPIs to measure the effectiveness of ISRM
Organizations should establish clear metrics and Key Performance Indicators to gauge the effectiveness of Information Security Risk Management. These could include:
- Security Posture Assessment and Improvement: Regularly evaluate the organization’s overall security posture, identify strengths and weaknesses, and track the reduction in risk exposure over time. This metric assesses both current status and trends in improving security resilience.
- Gap Identification and Mitigation: Monitor the number and severity of security gaps across various organizational areas alongside the effectiveness and timeliness of mitigation strategies implemented.
- Compliance Rate: Measure adherence to internal security policies and external regulatory requirements, ensuring continuous compliance.
- Risk Treatment Efficiency: Evaluate how efficiently risks are managed, including the time taken for risk mitigation and the effectiveness of the strategies employed.
- Business Continuity Plan (BCP) Testing: Regularly test BCPs to assess readiness and effectiveness in responding to security incidents or disruptions.
These KPIs and others offer tangible benchmarks to assess the performance of ISRM initiatives and guide continuous improvement.
How to report to stakeholders and management
ISRM reporting should be structured to provide clear, concise, and actionable information to stakeholders and management. Reports should:
- Highlight key risks, the status of ongoing initiatives, and areas requiring attention.
- Summarize compliance status and any incidents that have occurred.
- Include visual aids like charts and graphs to convey complex information quickly and effectively.
Ultimately, regular reporting keeps stakeholders informed and engaged in the organization’s risk management efforts.
How to use feedback for continuous ISRM improvement
Feedback is a critical component for continuous ISRM improvement. It should be solicited from various sources, including employees, IT staff, and external auditors.
Organizations should establish a culture where feedback is valued and acted upon, using it to refine risk management practices and enhance overall security posture.
Feedback can provide insights into the effectiveness of current strategies, reveal gaps in security measures, and suggest areas for enhancement. Organizations should establish a culture where feedback is valued and acted upon, using it to refine risk management practices and enhance overall security posture.
Conclusion and future directions
As we conclude our journey through ISRM, it’s time to look ahead. This section summarizes the key takeaways from our guide and anticipates the future trends in ISRM.
Key takeaways for building and maintaining an effective ISRM program
The key takeaways for building and maintaining an effective Information Security Risk Management program are clear:
- Implement a comprehensive strategy: A well-rounded approach, integrating risk management frameworks with security measures, is essential.
- Stay informed and compliant: Keeping abreast of evolving regulations and standards is crucial for effective ISRM.
- Foster a security culture: Cultivating a security-aware environment across the organization is vital for proactive risk management.
- Utilize collaborative GRC tools: Leveraging platforms like Isora GRC can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of your ISRM program.
- Regular monitoring and reporting: Ongoing assessment and transparent reporting are key to understanding and improving security posture.
Emerging trends in ISRM
Looking ahead, organizations should prepare for several emerging trends in ISRM:
- Increased automation: Advances in technology will continue to automate more aspects of risk management, making processes more efficient and data-driven.
- Greater focus on third-party risks: As ecosystems become more interconnected, managing third-party security risks will become increasingly important.
- Evolution of cyber threats: Cyber threats will continue to evolve, requiring organizations to stay vigilant and adapt their strategies accordingly.
- Regulatory changes: Expect continuous changes in compliance requirements, necessitating agile adaptation in ISRM practices.
- Emphasis on data privacy: With growing concern about data privacy, organizations must integrate privacy considerations into their ISRM strategies.
By staying aware of these trends and adapting proactively, organizations can ensure that their ISRM program remains robust, responsive, and aligned with the ever-changing information security landscape.
Dive into our research-backed resources–from product one pagers and whitepapers, to webinars and more–and unlock the transformative potential of powerfully simple GRC.
Learn More

















 Other Relevant Content
Other Relevant Content