 Table of Contents
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What does NIST 800-171 cover?
- NIST 800-171 Control Families
- What is the NIST 800-171 Basic Assessment?
- Do I need to conduct a NIST 800-171 Basic Assessment?
- What is the NIST 800-171 DoD Assessment Methodology?
- What is the Supplier Performance Risk System (SPRS)?
- How does the NIST 800-171 Basic Assessment relate to CMMC?
- What steps can I take to conduct a NIST 800-171 Basic Assessment?
- Conclusion
Central to the Cyber Security Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) is NIST SP 800-171. The NIST 800-171 Basic Assessment is a low-confidence self-assessment that follows the NIST 800-171 DoD Assessment Methodology.
As of November 30, 2020, all defense contractors must conduct a NIST 800-171 Basic Assessment and submit their score to the Supplier Performance Risk System (SPRS).
This Complete Guide from SaltyCloud covers everything you need to know about NIST 800-171, the NIST 800-171 Basic Assessment, the NIST 800-171 DoD Assessment Methodology, and the steps you can take to build a scalable, evidence-driven CMMC compliance process.
What does NIST 800-171 cover?
NIST 800-171 covers 110 security practices (also known as security controls or security requirements) across 14 control families for protecting the confidentiality of Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) outside of nonfederal information systems and organizations.
NIST 800-171 Control Families
| Family | Description |
| Access Control | Who has access to CUI, and are they supposed to have access? |
| Awareness and Training | Are employees who handle CUI adequately trained to treat CUI? |
| Audit and Accountability | Are records kept of who is accessing CUI, and can violators be tracked? |
| Configuration Management | How are networks and safety protocols built and documented? |
| Identification and Authentication | What users have access to CUI, and is their access managed? |
| Incident Response | What is the process in the event of a data breach, and how are appropriate parties notified? |
| Maintenance | What timeline exists for maintenance, and who is responsible? |
| Media Protection | How are digital and physical records safely stored and destroyed? |
| Personnel Security | How are employees screened before gaining access to CUI? |
| Physical and Environmental Protection | Where do you physically house CUI, and is access monitored and restricted? |
| Risk Assessment | Are risks periodically assessed, and are remediation plans created and enforced? |
| Security Assessment | Are security controls regularly assessed for effectiveness, and are remediation plans created and enforced? |
| System and Communications Protection | Is information regularly monitored and physically and logically separated from other internal networks? |
| System and Information Integrity | How quickly are possible threats detected, identified, and remediated? |
What is the NIST 800-171 Basic Assessment?
The NIST 800-171 Basic Assessment is a self-assessment designed to evaluate how well an organization implements CUI security requirements. It involves a detailed review of the organization’s System Security Plan (SSP), which documents how security controls are applied to protect CUI within the covered contractor information system(s) information systems. This assessment follows the NIST 800-171 DoD Assessment Methodology, as outlined in the document “Assessing Security Requirements for Controlled Unclassified Information.”
The result of a Basic Assessment is a “Low” confidence score, as it is self-generated by the contractor.
Do I need to conduct a NIST 800-171 Basic Assessment?
Yes, if you are part of the Defense Industrial Base (DIB).
As of November 30, 2020, the DFARS Interim Rule requires contractors and subcontractors working with the Department to perform a NIST 800-171 Basic Assessment. This self-assessment must be completed to evaluate compliance with the 110 NIST 800-171 security controls and ensure the protection of CUI.
Contractors are required to submit the resulting score to the SPRS as a condition for contract awards. This score provides visibility into a contractor’s cybersecurity posture, although it does not require a specific threshold for contract eligibility.
What is the NIST 800-171 DoD Assessment Methodology?
The NIST 800-171 DoD Assessment Methodology is a scoring system that allows the DoD to strategically assess a contractor’s implementation of NIST 800-171. The methodology is used for assessment purposes only and does not add any additional controls.
You score a NIST 800-171 Basic Assessment on a 110-point scale. Each of the 110 security practices in NIST 800-171 is assigned a “weighted subtractor” value. If you implement a practice, you get a certain amount of points, with a 110 as a perfect score.
Suppose you did not implement the control or only partially implemented the practice. In that case, you get a fraction of the points or subtracted points altogether, which means a negative score is possible. Some practices are worth 5 points, some 3, and some 1.
The DFARS Interim Rule does not require contractors to achieve a specific score. It only requires them to provide a score. However, it is unclear if and how acquisition officers might use the scores in best value determinations for contract awards and whether it will change once the CMMC final rule-making is complete.
Response Requirements
| Response | Requirement |
| Yes | Include a statement in the Security Assessment Report (SAR) and SSP explaining how the information system implements the requirement. |
| No | Include a statement in the SAR that explains why the security requirement is not met. Include a statement in the Plan of Action & Milestones (POA&M) which fully describes how the control will be met, how planned improvements will be implemented, and when the improvements will occur. |
| Partially | Include a statement in the SAR that explains why the security requirement is only partially met. A statement should also be included in the POA&M, which fully describes how the control will be met, how planned improvements will be implemented, and when the improvements will occur. |
| Does Not Apply | Include a statement in the SAR that explains why the security requirement does not apply to your operational environment. |
| Alternative Approach | Include a statement in the SAR the SSP that fully describes the alternative approach, how it is equally effective, and how the information system implements the requirement. |
What is the Supplier Performance Risk System (SPRS)?
The SPRS is a portal and database that will house all supplier and product performance information (PI) assessments for the DoD acquisition community to identify, assess, and monitor unclassified performance.
More specifically, it’ll be where contractors will submit their NIST 800-171 Basic Assessment scores and other documentation related to their contracts. Contractors will be able to update their scores as they improve over time.
How does the NIST 800-171 Basic Assessment relate to CMMC?
Conducting a NIST 800-171 Basic Assessment is an interim requirement during the five-year phased rollout of the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC). However, conducting a NIST 800-171 Basic Assessment will continue to be a requirement for CMMC Level 1 and CMMC Level 2 certifications. And to be certified at CMMC Level 2 and CMMC Level 3, contractors must meet all 110 security practices outlined in NIST 800-171.
While conducting a NIST 800-171 Basic Assessment is a requirement, and it is also a tool to help contractors identify gaps and prepare for certification.
What steps can I take to conduct a NIST 800-171 Basic Assessment?
Conducting a NIST 800-171 Basic Assessment can be challenging, especially depending on the complexity of your environment. To ensure success, your goal should be to build a scalable, evidence-driven risk assessment process within your organization. Using a GRC Assessment Platform like Isora GRC can help automate much of this process, making it easier to collect evidence, manage assessments, and ensure compliance.
Step 1: Read the official publications
Start by familiarizing yourself with the key resources:
- NIST SP 800-171, “Protecting Controlled Unclassified Information in Nonfederal Systems and Organizations,” which outlines all 110 security controls.
- NIST SP 800-171A, “Assessing Security Requirements for Controlled Unclassified Information,” which provides detailed assessment procedures for each control. This document helps guide how to conduct your assessment.
For organizations that lack in-house expertise, consider working with a Registered Provider Organization (RPO) to help navigate these resources.
Step 2: Identify key personnel
Successfully conducting a NIST 800-171 Basic Assessment requires collaboration. Identify key individuals responsible for managing assets, systems, and contracts involving FCI or CUI. This includes:
- Project leads handling awarded contracts.
- IT and cybersecurity personnel managing infrastructure and cybersecurity protocols.
Isora GRC can streamline communication by centralizing assessment tasks, assigning roles, and enabling secure collaboration between stakeholders.
Step 3: Scope your organization
Scoping your organization is a crucial step to identify where FCI and CUI are handled and to focus your compliance efforts. Instead of applying NIST 800-171 controls across your entire organization, you should isolate the systems, applications, and data flow that handle sensitive information.
Using a GRC Assessment Platform like Isora GRC enables you to:
- Maintain an inventory of assets, applications, and third-party vendor products to track where CUI and FCI are stored or processed.
- Track key details such as data classification, ownership, and other metadata for these assets, ensuring you focus compliance efforts on the most critical areas.
- Assign ownership and manage responsibilities across teams, simplifying collaboration during the self-assessment process.
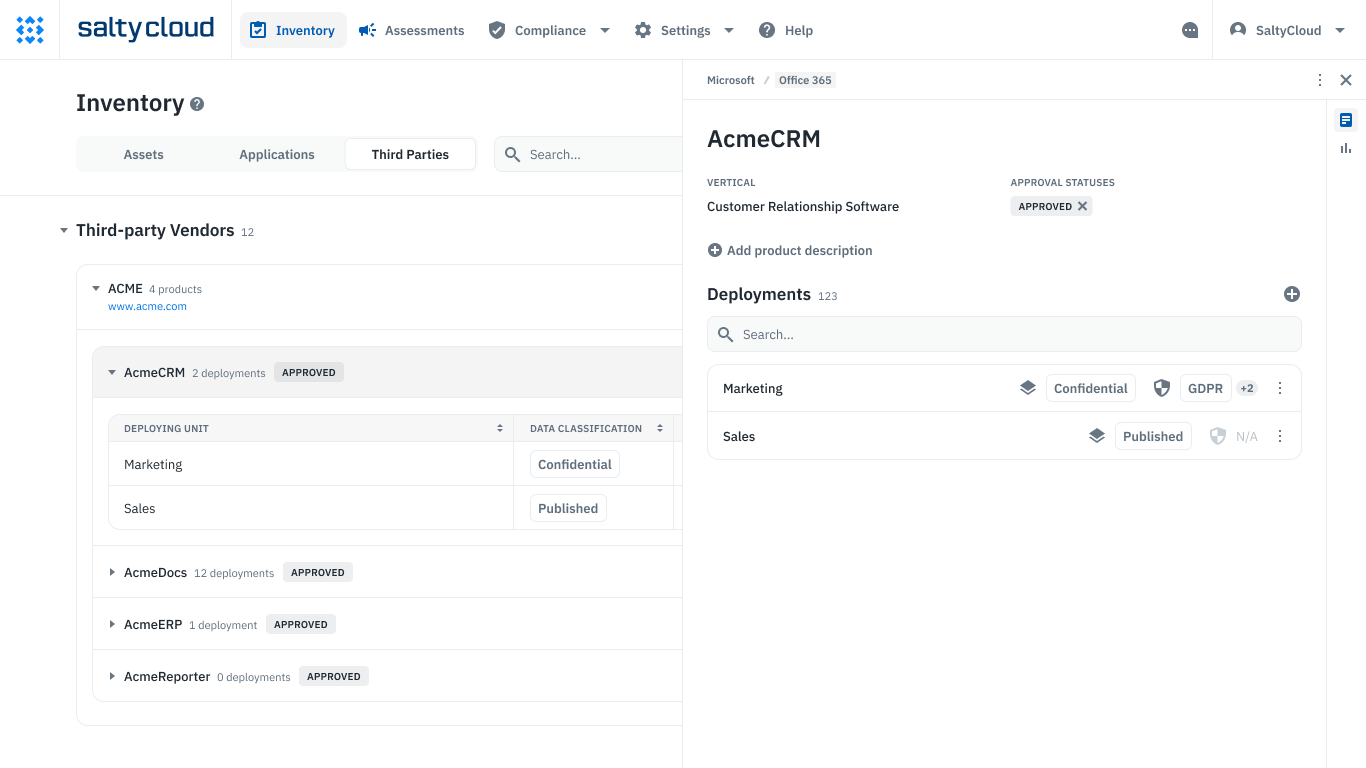
The third-party inventory section in Isora GRC
Step 4: Conduct the NIST 800-171 Basic Assessment
Work with your team to assess compliance with all 110 security controls. You can document whether controls are Implemented, Partially Implemented, or Not Implemented. Evidence collection is a crucial part of this process, such as gathering policies, procedures, and system configurations.
While spreadsheets or manual tracking can be used, they are inefficient and error-prone. With Isora GRC, you can automate the entire self-assessment process using automated questionnaires:
- Centralize evidence collection and track compliance across your organization.
- Ensure each security control is assigned to the correct stakeholders.
- Easily update, review, and manage assessment data in a secure platform.
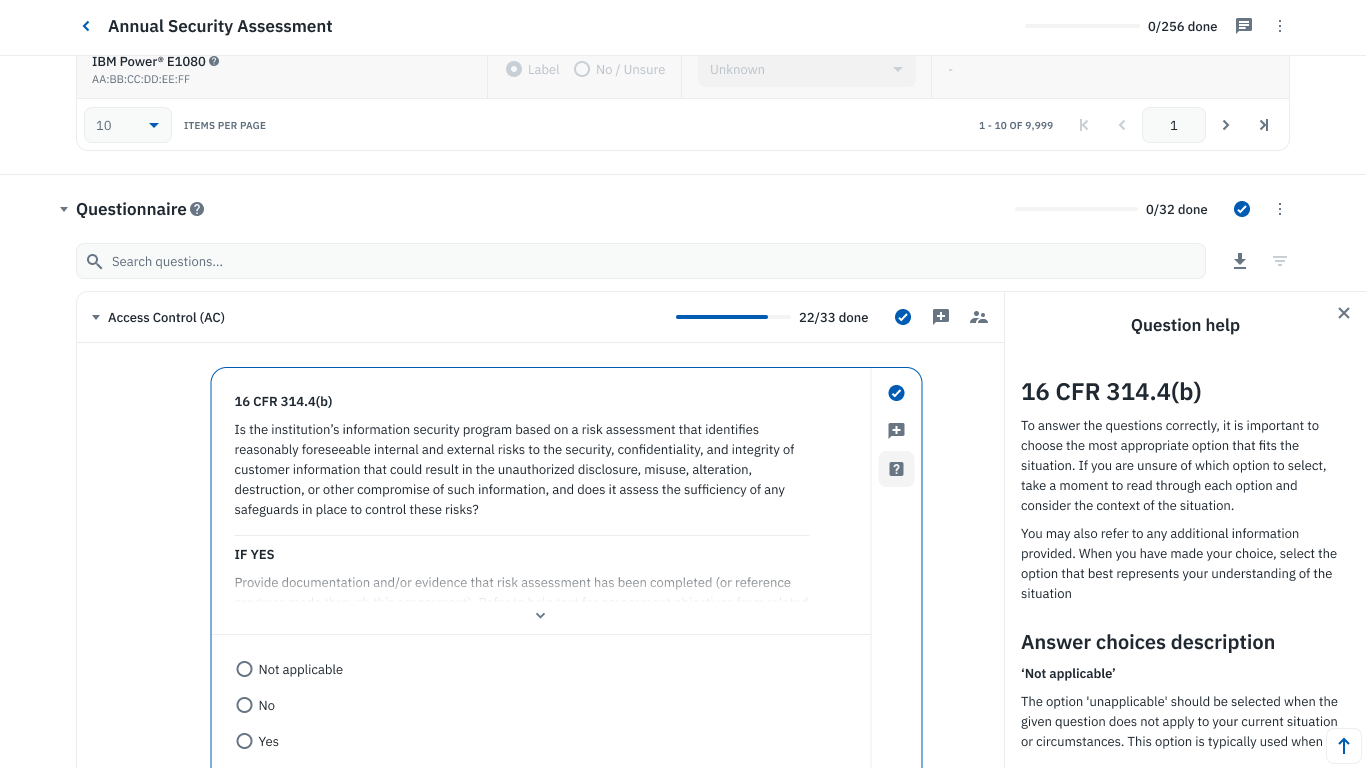
Collaborative questionnaire-based assessments in Isora GRC
Step 5: Calculate and submit your SPRS score
Once the assessment is complete, calculate your SPRS score using the NIST 800-171 DoD Assessment Methodology. Each control has a weighted subtractor value that determines the score. If you’re using a spreadsheet, you’ll need to manually calculate these scores.
However, Isora GRC can automate the scoring process, providing you with accurate results after completing your self-assessment. Once the score is calculated, submit it to the SPRS as required for contract awards.

NIST 800-171 SPRS score widget in Isora GRC
Step 6: Create a Plan of Action and Milestones (POA&M)
For controls that are Partially Implemented or Not Implemented, create a POA&M to document how and when you plan to address these gaps. While you aren’t required to submit the POA&M with your SPRS score, it is essential for improving your compliance status and is critical for CMMC certification.
Isora GRC can automatically generate a POA&M based on your assessment results, helping you track progress and remediation actions.

POA&M Export in Isora GRC
Step 7: Establish a repeatable process
Compliance with NIST 800-171 and future CMMC requirements is an ongoing process. Establish a repeatable and scalable approach for conducting regular self-assessments. This ensures your organization remains compliant and ready for new cybersecurity requirements from the DoD.
Using Isora GRC, you can automate future assessments, centralize evidence, and track compliance over time, making it easier to stay on top of evolving requirements.
Conclusion
Conducting a NIST 800-171 Basic Assessment is an essential part of meeting regulatory compliance for contractors in the DIB. By following the assessment methodology and submitting your score to the SPRS, you ensure that your organization is aligned with the Department’s cybersecurity requirements.
Using a GRC Assessment Platform like Isora GRC allows you to automate questionnaires, centralize evidence collection, and manage asset inventories, making regulatory compliance more streamlined and scalable. As cybersecurity standards evolve, establishing a repeatable assessment process will be crucial for maintaining compliance and securing future DoD contracts.
Dive into our research-backed resources–from product one pagers and whitepapers, to webinars and more–and unlock the transformative potential of powerfully simple GRC.
Learn More

















 Other Relevant Content
Other Relevant Content